Radiation protection Sector






Radiation Shielding Material
Request InformationProduct Details
Lead-Boron Polyethylene: Advanced Composite for Neutron and Gamma Shielding
Once a specialized material, lead-boron polyethylene is now emerging as a mainstream solution in radiation shielding—driven by its dual functionality against neutrons and gamma rays, lightweight nature, and adaptability to evolving regulatory and engineering demands. With global growth in nuclear energy, precision radiotherapy, space exploration, and industrial radiography, this composite is positioned to capture significant share in the multibillion-dollar shielding market.
Core Product Variants & Composition
1. Boron Polyethylene (Neutron-Optimized)
Base Matrix: HDPE or UHMWPE
Additives: Boron compounds (B₄C, B₂O₃, borax, boric acid)
Function: Efficient thermal neutron absorption via 10B(n,α) reaction; hydrogen moderates fast neutrons.
2. Lead-Boron Polyethylene (Mixed-Field Shielding)
Base Matrix: Boron-loaded polyethylene
Additives: Lead compounds (PbCO₃, PbO) + boron compounds
Function: Simultaneous attenuation of neutrons (via B/H) and gamma/X-rays (via Pb photoelectric/Compton effects).
3. Boron Carbide Polyethylene (High-Performance Neutron)
Base Matrix: HDPE or UHMWPE
Additives: High-purity B₄C powder (≥95% 10B enrichment available)
Function: Premium neutron shielding with enhanced thermal stability and reduced secondary gamma emission.
Key Technical Advantages
Dual Radiation Shielding: – Neutrons: Moderated by H in PE, absorbed by 10B (σ = 3,840 barns). – Gamma/X-rays: Attenuated by Pb (Z = 82); low-energy secondary gammas from B capture are easily shielded.
Lightweight: Density 1.0–2.0 g/cm³ vs. concrete (~2.4 g/cm³) or lead (~11.3 g/cm³), reducing structural load and transport costs.
Mechanical Robustness: High impact resistance, flexural strength, and abrasion tolerance inherited from polyethylene matrix.
Design Flexibility: – Additive loading: 2–77 wt% (boron and/or lead) – Thickness: 5–260 mm (standard); >260 mm via seamless splicing – Panel size: up to 6,000 mm × 2,500 mm
Processability: Easily machined (cut, drilled, milled, chamfered); limited thermoforming feasible.
Environmental Stability: Resistant to moisture, corrosion, solvents, and UV degradation within operational temperature ranges (–40°C to +80°C typical).
Low Activation: Generates minimal residual radioactivity with short half-lives compared to metallic shields.
Material Uniformity: Homogeneous dispersion of additives ensures consistent shielding performance across large panels.
Cost Efficiency: Lower lifecycle cost due to ease of installation, durability, recyclability (non-lead variants), and reduced logistics burden.
Environmental Compliance: Significantly reduces lead usage versus pure lead shielding—especially in B-only or B₄C formulations.
Primary Applications
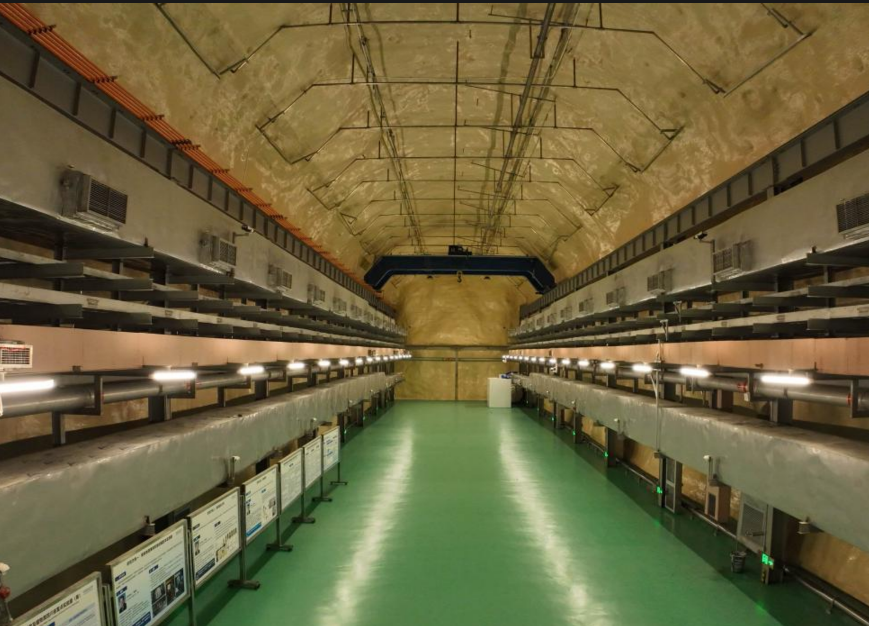
Nuclear Energy: Reactor biological shields, spent fuel pools, transport casks, glove boxes, hot cells.
Medical: LINAC/particle therapy bunkers, PET/SPECT dispensing shields, isotope storage, diagnostic room lining.
Industrial: Neutron radiography/CT enclosures, well logging source containers, irradiation facilities.
Research & Education: Laboratory shielding walls/doors, detector collimators, calibration source housings.
Aerospace & Security: Cosmic neutron shielding for spacecraft electronics; shielding for radiation portal monitors.
Emergency Response: Deployable mobile shielding barriers and containment units.
Selection Guidelines
Pure neutron fields: Use Boron PE or Boron Carbide PE (B₄C preferred for high stability or elevated temperatures).
Mixed neutron + gamma fields: Lead-Boron PE is required for comprehensive attenuation.
Weight-sensitive applications: All variants offer advantages over concrete or lead; B₄C PE provides best strength-to-density ratio.
High-temperature environments (>80°C): Boron Carbide PE exhibits superior thermal resistance.
Quality Assurance
Rigorous process control ensures uniform additive distribution, density consistency, and absence of voids or delamination.
Shielding performance validated via Monte Carlo simulation (e.g., MCNP) or third-party testing per customer requirements.
Compliant with relevant standards including ASTM, ISO, and national nuclear safety guidelines.